When it comes to automatic transmissions, most drivers don’t think about clutches. After all, clutches are usually associated with manual transmissions, where the driver manually engages and disengages gears. But did you know that both continuously variable transmissions (CVTs) and traditional automatic transmissions use clutches in different ways?
How Traditional Automatic Transmissions Use Clutches
Traditional automatic transmissions operate using a combination of planetary gear sets, hydraulic systems, and a torque converter. Unlike a manual transmission, which relies on a single clutch to engage and disengage gears, an automatic transmission has multiple clutch packs inside. These clutches work together to engage and disengage different gears based on the vehicle’s speed and load.
When you accelerate, hydraulic pressure activates specific clutch packs, allowing the transmission to shift gears automatically. This process ensures a seamless driving experience without requiring manual gear changes. The torque converter, which connects the engine to the transmission, also uses a type of clutch—called a lock-up clutch—to improve fuel efficiency at higher speeds.
Over time, these internal clutches can wear out due to heat, friction, and fluid breakdown. That’s why regular transmission maintenance, including fluid changes, is crucial to keeping your automatic transmission running smoothly.
Do CVT Transmissions Have Clutches
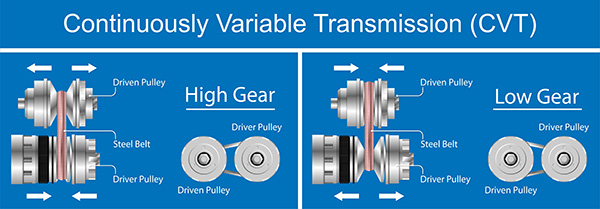
Unlike traditional automatic transmissions, CVTs don’t use fixed gears. Instead, they rely on a system of pulleys and a belt or chain to provide an infinite number of gear ratios. This design allows CVTs to maintain the engine at optimal performance levels, improving fuel efficiency and delivering a smoother driving experience.
Since CVTs don’t have gears in the conventional sense, they also don’t use multiple clutch packs like traditional automatics. However, most CVTs still have a clutch—typically a start clutch or a torque converter—to engage and disengage power from the engine to the transmission.
Some CVTs use a wet clutch system, which is immersed in transmission fluid, while others use a dry clutch, similar to those found in manual transmissions. The type of clutch used depends on the specific CVT design and manufacturer.
Key Differences Between CVT and Automatic Transmissions
- Number of Clutches – Traditional automatics use multiple clutch packs, while CVTs typically have only one clutch or a torque converter.
- Gear Shifting – Automatic transmissions shift between fixed gears using clutches, whereas CVTs use a continuous range of gear ratios without actual shifting.
- Maintenance Needs – Since CVTs don’t rely on multiple clutches, they generally experience less wear in that area, but they require specialized CVT fluid changes to prevent belt or chain wear.
Signs of Transmission Wear or Failure
Regardless of whether your vehicle has a CVT or a traditional automatic transmission, certain warning signs may indicate clutch-related issues. These include:
- Slipping gears – If your vehicle struggles to stay in gear or shifts erratically, it could be due to worn clutch packs in an automatic transmission or a failing start clutch in a CVT.
- Delayed engagement – If there’s a delay when shifting from Park to Drive, the clutches or torque converter may be wearing out.
- Shuddering or jerking – A failing clutch system can cause noticeable vibrations, especially when accelerating.
- Burning smell – Overheated transmission fluid can indicate excessive clutch wear or internal damage.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s important to get your transmission checked by a professional as soon as possible.
Maintaining Your Transmission for Long-Term Reliability
Routine transmission maintenance is the key to keeping both CVTs and traditional automatic transmissions in top condition. Here are a few essential tips:
- Follow the manufacturer’s fluid change schedule – CVTs require specialized fluid, so make sure to use the correct type recommended for your vehicle.
- Check for transmission leaks – Low fluid levels can lead to clutch wear and overheating.
- Avoid aggressive driving – Rapid acceleration and sudden braking can strain the transmission and cause premature clutch wear.
- Listen for unusual noises – Grinding, whining, or clunking sounds can signal internal transmission problems.
If you’re in Berkeley, CA, and need professional transmission maintenance or diagnostics, trust us to assess and address any transmission concerns before they become costly repairs.
Don’t wait until your transmission fails! Whether you have a CVT or a traditional automatic, routine maintenance is essential. Visit The Model Garage in Berkeley, CA, for expert transmission service. Schedule an appointment today!